Boosting production line efficiency: a guide on improving production output
Production efficiency is the cornerstone of success in manufacturing. It measures the effectiveness of resource utilization in the manufacturing process, aiming to maximize output while minimizing costs and waste. The role of a Production Manager is instrumental in achieving this efficiency, as they ensure that manufacturing operations stay on track, within budget, and meet the desired output objectives.
Research conducted in collaboration with Visual Components reveals that checking daily production output is a top priority for manufacturing supervisors, emphasizing its vital role in manufacturing operations. This practice enables the tracking of the quantity of goods or products that a manufacturing process produces each day. The primary operational aim is to achieve the daily production output target, which sets the day’s benchmark and directs the team’s efforts. Any deviation or failure to meet this target necessitates immediate intervention. Production output is a crucial key performance indicator (KPI) that reflects the efficiency, effectiveness, and overall health of the manufacturing process.
In this article, we will delve deeper into:
- Understanding production output as a KPI
- Common challenges limiting production line efficiency
- How to improve production line efficiency and output
Understanding production output as a KPI
In a closed-loop production management model, Production Managers are tasked with managing the day-to-day operations of the production system to meet the company’s requirements. The production system allows for the collection of production data which then forms KPIs that provide insight into current production performance.
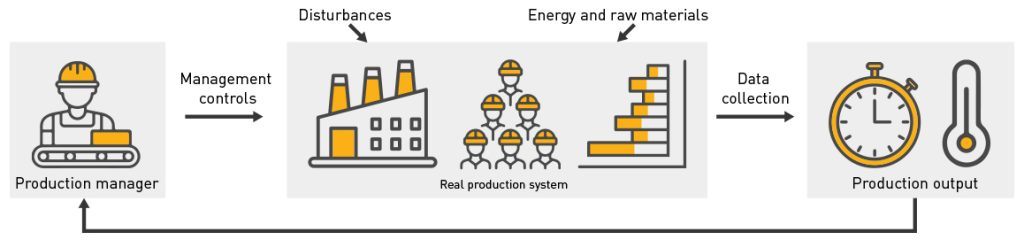
One such KPI is production output, which measures the volume of quality-approved components produced in a given period of time. Calculating production output as a KPI in manufacturing involves several key metrics that provide a comprehensive view of the production process.
Factory production volume [quantity/time period]
This metric measures the total amount of products or kilograms produced by the factory in a given time period. It’s calculated by simply counting the number of units produced and dividing by the time period. This gives you a production rate that can be tracked over time to identify trends and make forecasts.
Good quality parts [quantity]
This metric focuses on the number of units produced by the factory that also meet quality standards. It’s calculated by inspecting the units produced and counting how many meet the required quality criteria. This metric is critical to maintaining high product quality and customer satisfaction.
Planned production output vs. actual production output [percent]
This metric compares the number of products the factory planned to produce to the number actually produced. It’s calculated by dividing the actual output by the planned output and multiplying by 100 to get a percentage. This metric helps identify any discrepancies between planning and execution, which can inform future planning processes.
Job shop value-added hours [percent]
This metric is used in project manufacturing. It compares the planned value-added hours with the actual value-added hours. For example, if 1000 value-added hours were planned and 800 value-added hours were completed, the metric is 80%. This metric helps assess the efficiency of the value-added process and can guide improvements in scheduling and execution.
In project-based or job-shop manufacturing, production output can also be measured as a percentage of project completion. For example, in shipbuilding, project completion % can be measured and compared to project schedule %. This provides a clear picture of project progress and can help identify any delays or inefficiencies in the production process.
These metrics provide a holistic view of the production process. A high production output suggests a smooth, efficient manufacturing process, while a low output may hint at issues like equipment malfunctions, supply chain disruptions, or labor inefficiencies. This KPI enables managers to monitor performance, identify areas for improvement, and make informed decisions to optimize production output.
Common challenges limiting production line efficiency
The ability to produce goods swiftly, without compromising on quality, is what sets apart leading manufacturers from the rest. However, achieving optimal production line efficiency is no easy feat. Manufacturing production managers often face several challenges that affect production output.
Resource constraints
Space or equipment constraints in the factory can limit available production capacity. Regular maintenance is necessary to prevent equipment failure and unexpected downtime. However, unexpected machine breakdowns can still occur, leading to production halts and delays.
Shortage of raw materials
Disruptions in the supply chain can lead to a shortage of raw materials to the factory or shop floor. This can result in increased costs, delays, and a decrease in productivity.
Quality issues
Ensuring the quality of products is a constant challenge. High defect rates and poor quality can lead to high return rates and damage the company’s reputation.
Workforce challenges
This includes unexpected personnel illnesses and unmotivated workers. The need for skilled, motivated workers is crucial in maintaining production efficiency. Unplanned absences can disrupt the production schedule, while unmotivated workers can lead to decreased productivity and quality.
Inaccurate demand forecasts and unrealistic demands
Accurate demand forecasting is crucial for avoiding overproduction or stockouts. However, inaccurate forecasts can lead to inventory issues and waste. Additionally, unrealistic demands set by company management can put undue pressure on the production process, leading to quality issues and employee burnout.
Improving production line efficiency and output with simulation and OLP
Watch our on-demand webinar to learn how manufacturing production teams can optimize production output with factory simulation and robot offline programming (OLP).
In this on-demand webinar, Visual Components’ industry experts, Mikael Saksi and Jyri Luhtio explore topics such as the estimated industrial robotics market value, common challenges in production management, and the role of simulation and OLP in taking manufacturing projects from concept to reality. The on-demand webinar also features case studies demonstrating successful implementations and a Q&A session covering various aspects of Visual Components’ simulation and OLP software.
Further reading
An introduction to virtual commissioning
Virtual commissioning is reshaping the manufacturing landscape by employing computer simulations for testing and optimizing production systems before they're physically built. This approach not only simplifies the setup process and...
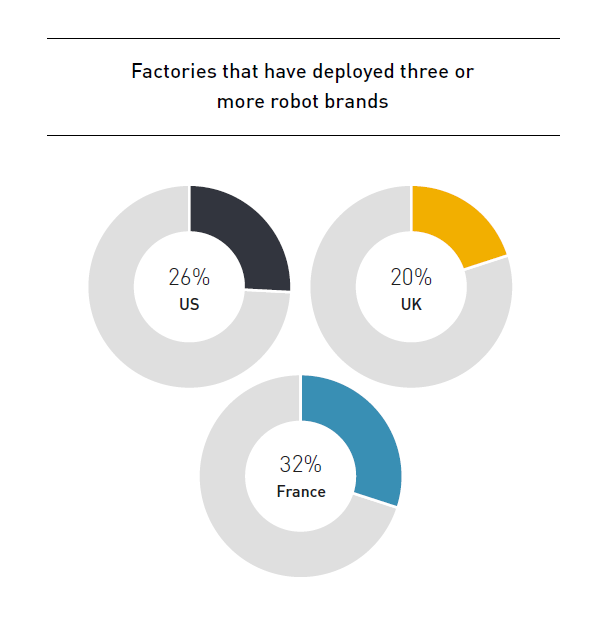
Are manufacturers really ready for the digital era? (survey results)
Legacy equipment and outdated practices can seem like relics from another age, especially as the world zooms ahead with digital innovations. Yet, they're more prevalent in the manufacturing sector than...

Considerations for CIOs in 2023: navigating sustainability, resilience, and human needs
In today's rapidly changing manufacturing landscape, Chief Information Officers (CIOs) face the challenge of navigating cost pressures while balancing human needs, the supply chain, and new production strategies and technologies.